Views: 222 Author: Wendy Publish Time: 2025-12-25 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● What Is a Resistive Touch Screen?
● Why Choose Resistive Touch Screen Technology?
● Resistive Touch Screen Market Landscape in Vietnam
● Typical Applications of Resistive Touch Screen in Vietnam
>> Industrial Automation and Machinery
>> Food Processing and Pharmaceuticals
>> Retail, POS, and Service Kiosks
>> Transportation, Logistics, and Warehousing
● Typical Company Roles in Vietnam's Resistive Touch Screen Ecosystem
● Advantages of Resistive Touch Screen Solutions for Industrial Buyers
>> Cost and Design Flexibility
>> Robustness and Predictable Behavior
● Important Technical Parameters When Specifying Resistive Touch Screen Products
● How to Evaluate Vietnam-Based Partners for Resistive Touch Screen Projects
>> Product Portfolio and Experience
>> Engineering and Customization Capabilities
>> Quality Management and Certification
>> Logistics, After‑Sales, and Long‑Term Support
● Practical Sourcing Workflow for Overseas Buyers
● FAQ
>> 1. Is a Resistive Touch Screen still a good choice for new industrial projects?
>> 2. Can Vietnamese suppliers provide fully customized HMIs with Resistive Touch Screen fronts?
>> 3. What information should I include in an RFQ for Resistive Touch Screen devices?
>> 4. How do I compare Resistive Touch Screen and capacitive touch for my project?
>> 5. What are common risks when sourcing Resistive Touch Screen products, and how can they be reduced?
Vietnam is steadily becoming a practical sourcing base for industrial displays, HMI panels, and Resistive Touch Screen solutions that serve both domestic and export markets. For global OEMs and system integrators, working with Vietnamese partners can combine cost-effective assembly in Vietnam with mature Resistive Touch Screen components from China, Japan, and other hubs.[1]
Vietnam's electronics industry is growing quickly, supported by multinational manufacturers, regional distributors, and local system integrators that assemble HMIs, panel PCs, and touch monitors. For Resistive Touch Screen buyers, Vietnam offers competitive labor costs, improving logistics, and close cooperation with Asian touch panel producers.[2] For international buyers sourcing from Resistive Touch Screen manufacturers and suppliers, understanding the local producers, product ranges, and quality standards is the key to successful cooperation.

A Resistive Touch Screen is a pressure-sensitive touch panel built from two conductive layers separated by small spacer dots; when pressed, the layers contact and the controller calculates the touch point. Unlike capacitive technology, a Resistive Touch Screen works with a bare finger, gloved hand, stylus, or even non-conductive objects, which makes it attractive for industrial and medical environments.[3]
A typical industrial Resistive Touch Screen module consists of a PET or glass top layer, an ITO-coated bottom layer, a controller board, and an interface such as USB or RS232 to the host system. Many Resistive Touch Screen products support 4‑wire or 5‑wire structures; 5‑wire designs often deliver better long-term stability in harsh conditions.[4]
A Resistive Touch Screen is often selected when functional reliability matters more than multi‑touch gestures or sleek consumer styling. Because the touch signal depends on physical pressure, a Resistive Touch Screen can be operated with tools, gloves, or stylus pens even in dusty, wet, or noisy industrial environments.[3]
Compared with many projected capacitive solutions, a Resistive Touch Screen can be more cost‑effective in small-to-medium sizes and is easier to integrate with legacy embedded boards using simple interfaces. Although optical clarity and gesture support may be higher with capacitive panels, a robust Resistive Touch Screen frequently offers the best balance of cost, durability, and input flexibility in industrial projects.[5][3]
Vietnam's touch and display market is strongly influenced by regional supply chains, especially those in China, South Korea, and Japan. Many of the Resistive Touch Screen panels used in Vietnam are sourced from specialized manufacturers abroad and then integrated locally into HMIs, panel PCs, kiosks, and other equipment.[2]
Local system integrators and solution providers focus on enclosure design, industrial certification, software integration, and on‑site service. In many cases, the final product shipped from Vietnam combines a foreign-made Resistive Touch Screen sensor with a locally assembled metal housing, power electronics, and application‑specific firmware.[2]
In Vietnamese factories, a Resistive Touch Screen is widely used on control panels, operator terminals, and industrial PCs. Operators can monitor real-time production data, modify setpoints, and run diagnostics through Resistive Touch Screen HMIs mounted directly on machinery or walls.[3][2]
Sectors such as electronics assembly, packaging, rubber and plastics, and metal fabrication often rely on Resistive Touch Screen HMIs because they work reliably even when operators wear gloves or have oily hands. A properly sealed Resistive Touch Screen with an IP65 or higher front can withstand dust, vibration, and occasional splashes common in industrial workshops.[2][3]
Vietnam's expanding food processing and pharmaceutical sectors require strict hygiene and frequent cleaning of equipment surfaces. In such environments, stainless‑steel panel PCs with Resistive Touch Screen fronts are popular because they allow operators to control processes while wearing thick protective gloves.[2]
A Resistive Touch Screen panel used in wash‑down zones is typically paired with a waterproof enclosure and often a flat front design for easier cleaning. This configuration reduces dirt traps and allows high‑pressure cleaning around the Resistive Touch Screen without compromising functionality.[2]
Although many modern retail systems use capacitive touch, a Resistive Touch Screen still appears in cost‑sensitive POS devices, ticket machines, and self‑service kiosks. These devices may not require multi‑touch or gesture capabilities, so a single‑touch Resistive Touch Screen can deliver adequate performance at a lower cost.[5][3]
Service kiosks deployed in bus stations, parking facilities, hospitals, or government offices often prioritize durability over high-end consumer‑style interaction. Here, the reliability and predictable behavior of a Resistive Touch Screen can make maintenance simpler over the long term.[3][2]
In trucks, forklifts, and logistics terminals, vibration and temperature changes can be significant. Rugged in‑vehicle computers and handheld terminals often use a Resistive Touch Screen to allow drivers and warehouse staff to operate systems with gloves or stylus pens.[3][2]
Warehouse management systems, barcode scanning stations, and loading dock HMIs can all integrate a Resistive Touch Screen panel designed to withstand frequent tapping and rough use. This approach ensures that logistics operations continue smoothly even under challenging conditions.[3][2]
While Vietnam is not yet a global center of raw Resistive Touch Screen sensor production, the country hosts several types of companies involved in the value chain. Their roles can be broadly grouped into component suppliers, system integrators, and OEM/ODM manufacturers.[2]
1. Local system integrators
These firms design complete solutions such as industrial HMIs, panel PCs, or interactive kiosks that embed a Resistive Touch Screen as part of a wider system. They work closely with foreign component providers and domestic end users to adapt each Resistive Touch Screen product to local site conditions.[2]
2. Panel PC and HMI assemblers
Some companies specialize in assembling industrial computers with integrated Resistive Touch Screen fronts, suitable for automation, food processing, or logistics applications. They select compatible mainboards, power supplies, and enclosures and then combine them with the right Resistive Touch Screen module.[2]
3. Distributors and traders
Local distributors handle imports of Resistive Touch Screen sensors, controller boards, TFT displays, and finished touch monitors. They maintain stock, provide basic technical support, and coordinate with overseas manufacturers when a project requires customized Resistive Touch Screen specifications.[2]
4. Design and engineering service companies
These firms focus on mechanical, electrical, and software design for touch-based equipment. In projects where a Resistive Touch Screen is the main interface, they help optimize the housing, sealing, and user interface layout to ensure good ergonomics and reliability.[2]
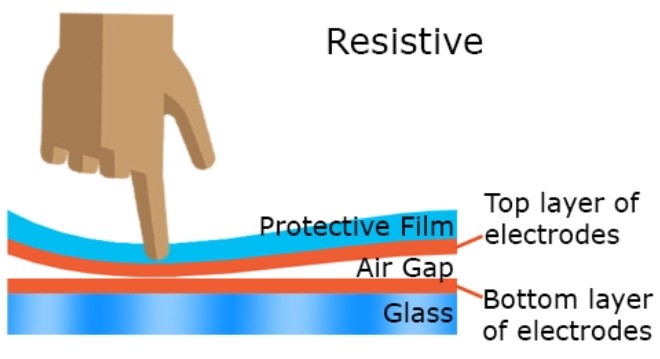
Because a Resistive Touch Screen registers pressure rather than the electrical properties of the human body, it can be operated by virtually any pointed object. This is a key benefit in industries where operators must wear thick gloves for safety, hygiene, or comfort.[3]
In maintenance and field service applications, engineers can use stylus pens on Resistive Touch Screen devices to tap small icons or enter data precisely. This helps maintain accuracy even when the interface layout is dense or the operator is working in tight spaces.[3]
A Resistive Touch Screen is generally more cost‑effective than a high-end projected capacitive panel of similar size, particularly in industrial ranges below large digital signage formats. This price advantage allows OEMs to deploy bigger screens or add redundant terminals without dramatically increasing project budgets.[5]
Resistive Touch Screen modules also support a wide range of aspect ratios and resolutions, from legacy 4:3 panels to widescreen 16:9 and 16:10 formats. This flexibility is important when upgrading older equipment, because a modern Resistive Touch Screen can often be matched mechanically to the cut‑outs and bezels of previous generations.[4]
A Resistive Touch Screen tends to respond consistently under varied environmental conditions, such as humidity and electrical noise. While proper sealing and controller design are still necessary, the underlying principle of physical contact between layers makes the response less dependent on skin conductivity.[3]
In demanding areas like factories, cold rooms, or outdoor enclosures, the predictable behavior of a Resistive Touch Screen can be more valuable than advanced multi‑touch gestures. This simplicity also reduces the learning curve for operators who just need reliable single‑touch control.[3]
When sourcing from Vietnam-based suppliers, buyers should clearly define the expected technical parameters of their Resistive Touch Screen assemblies. A detailed specification reduces the chance of mismatched panels, unexpected limitations, or failures in the field.[2]
Key parameters include:
- Screen size and aspect ratio
Decide whether the Resistive Touch Screen will be used with 4:3, 5:4, or widescreen displays and confirm the active area dimensions. Ensure that the panel size fits the planned enclosure cut‑out and that the viewing distance and font sizes are suitable for operators.[4]
- Touch structure (4‑wire vs 5‑wire)
Clarify whether a 4‑wire or 5‑wire Resistive Touch Screen is required, considering target lifetime, calibration stability, and controller compatibility. Industrial users often prefer 5‑wire designs for high usage environments where long-term drift must be minimized.[4]
- Optical properties
Specify transmittance, anti‑glare or anti‑reflective coatings, and any need for chemically strengthened or tempered cover glass on top of the Resistive Touch Screen. Good optical design ensures that brightness and contrast remain acceptable even after adding multiple protective layers.[4]
- Electrical and interface requirements
Confirm the interface type (USB, RS232, or others), supply voltage, EMC performance, and required operating system drivers for the Resistive Touch Screen controller. This information must be aligned with the industrial PC, PLC, or embedded board used in the project.[5]
- Environmental and mechanical constraints
Communicate the expected temperature range, humidity, shock, vibration, and exposure to liquids or chemicals around the Resistive Touch Screen. Appropriate sealing gaskets, front glass thickness, and mounting methods depend directly on these conditions.[2]
First, review the supplier's catalog of touch products and check whether Resistive Touch Screen devices form a meaningful part of their business. Look for clear descriptions of supported sizes, wiring structures, controller options, and IP ratings.[2]
Experienced partners can show reference projects in automation, food processing, logistics, healthcare, or other sectors that use similar Resistive Touch Screen requirements. Case studies and photos help confirm that the company can deliver rugged equipment rather than only office‑grade hardware.[2]
A strong partner can adapt the front panel, housing, and firmware around the Resistive Touch Screen to match specific project demands. This might include custom logos, special mounting brackets, extended cables, or tailored touch behavior.[2]
Check whether the engineering team can provide 2D drawings, 3D models, and driver packages quickly, and whether they can support multiple languages in the HMI interface. Good communication between your engineers and the supplier's technical staff is critical to a smooth integration of the Resistive Touch Screen into your equipment.[2]
Ask about quality standards and certifications used in the design and production of equipment that includes a Resistive Touch Screen. For example, ISO-based quality systems, EMC testing, and environmental tests indicate more mature procedures.[2]
If your application involves food, pharmaceuticals, or transportation, verify any additional regulatory requirements that the Resistive Touch Screen system must meet. This may include documentation around materials, cleaning compatibility, or safety aspects.[2]
Confirm lead times for sample and mass orders, as well as the supplier's approach to warehousing replacement Resistive Touch Screen panels or complete devices. Well-planned logistics can reduce downtime if a field unit needs repair or replacement.[2]
Ask about warranty terms, RMA procedures, and the availability of local service partners or remote troubleshooting. Long-term availability of compatible Resistive Touch Screen modules is especially important for industrial equipment that will operate for many years.[2]
For overseas buyers, a structured workflow improves the chances of a successful cooperation with Vietnam-based partners on Resistive Touch Screen projects. A typical process includes the following stages.[2]
1. Requirement definition
Clearly document display size, resolution, brightness, touch type (Resistive Touch Screen details), environmental conditions, and required certifications.[2]
2. Supplier shortlisting and RFQ
Identify several potential partners and send a detailed RFQ covering all Resistive Touch Screen and system-related parameters.[2]
3. Sample development and testing
Receive engineering samples or small pilot batches of HMIs or panel PCs using the specified Resistive Touch Screen. Test them under real operating conditions to validate performance and durability.[2]
4. Design refinement
Provide feedback and request improvements in areas such as bezel design, touch sensitivity, or screen readability to optimize the Resistive Touch Screen integration.[2]
5. Mass production and quality monitoring
Once designs are frozen, proceed to volume production with agreed testing procedures and inspection standards for each Resistive Touch Screen batch.[2]
6. Ongoing support and upgrades
Maintain communication with the supplier to manage firmware updates, new size introductions, or future transitions between Resistive Touch Screen generations.[2]
Vietnam is an increasingly attractive location for sourcing industrial HMIs, panel PCs, and kiosk systems that integrate reliable Resistive Touch Screen interfaces. By combining imported touch components with local engineering and assembly, Vietnam-based partners can deliver solutions tailored to regional and global industrial requirements.[2]
For buyers, the key to success is a clear technical specification, thorough supplier evaluation, and structured project management that covers the full life cycle of each Resistive Touch Screen product. With the right cooperation model, Vietnam can play a strategic role in a diversified supply chain for long‑life Resistive Touch Screen devices used across automation, food processing, logistics, healthcare, and public services.[2]

Yes, a Resistive Touch Screen remains a strong option for industrial projects that require glove operation, stylus input, or work in harsh environments where cost and robustness outweigh multi‑touch. Many factories continue to specify Resistive Touch Screen HMIs because they are predictable, easy to integrate, and widely available.[3]
Many Vietnam-based integrators and assemblers can deliver custom HMIs and panel PCs using standard or custom-sized Resistive Touch Screen panels. They can often adapt the enclosure, connectors, firmware, and branding to match specific OEM requirements.[2]
An effective RFQ should include required screen size, resolution, touch structure (4‑wire or 5‑wire Resistive Touch Screen), environmental conditions, interfaces, and certifications. Adding drawings, photos of existing equipment, and a brief usage description helps suppliers propose accurate solutions faster.[2]
When comparing technologies, consider input method, environment, and cost: a Resistive Touch Screen offers flexible glove and stylus use at lower cost, while capacitive touch delivers better optics and multi‑touch. If your operators often wear heavy gloves or work in electrically noisy areas, a Resistive Touch Screen may provide more reliable performance.[3]
Common risks include incomplete specifications, insufficient testing, and unclear expectations for lifespan and support of the Resistive Touch Screen module. These risks can be reduced by detailed technical documentation, pilot runs, and clear agreements on quality, warranty, and long-term availability.[2]
[1](https://www.perplexity.ai/search/615b0f0a-6fe1-4e86-87e3-766544862312)
[2](https://www.perplexity.ai/search/4bb0cf45-4074-43dd-858b-d20dbc0f534b)
[3](https://www.perplexity.ai/search/2a13bace-290b-40c1-932c-2335bbff98da)
[4](https://www.perplexity.ai/search/4c69768c-a7a6-46df-a689-72902eb72d9a)
[5](https://www.perplexity.ai/search/e67928ad-14a8-4811-af85-fa97223e4ef3)
Top Resistive Touch Screen Manufacturers and Suppliers in Turkey
Top Resistive Touch Screen Manufacturers and Suppliers in Vietnam
Top Resistive Touch Screen Manufacturers and Suppliers in South Korea
Top Resistive Touch Screen Manufacturers and Suppliers in Japan
Top Resistive Touch Screen Manufacturers and Suppliers in Italy
Top Resistive Touch Screen Manufacturers and Suppliers in Portugal
Top Resistive Touch Screen Manufacturers and Suppliers in Spain